Migration Guide
Migrating to Cypress CFG_VERSION
This guide details the changes and how to change your code to migrate to Cypress CFG_VERSION. [See the full changelog for CFG_VERSION](/guides/references/changelog#CFG_VERSION_CHANGED_TO_HASH.
Configuration file changes
Cypress now supports JavaScript and TypeScript configuration files! By default,
Cypress will automatically load a cypress.config.js or cypress.config.ts
file in the project root if one exists. The
Configuration guide has been updated to
reflect these changes, and explains them in greater detail.
The cypress.json configuration file is now deprecated. Documentation for
cypress.json is now available in the
Legacy Configuration guide. Support
for cypress.json will be removed in a future version of Cypress.
Related notes:
- If no config file exists when you open the Cypress App, a
cypress.config.jsfile will now be auto-generated for you. - A
defineConfighelper function is now exported by Cypress, which provides automatic code completion for configuration in many popular code editors. - Many pages and examples throughout the documentation have been updated to show
configuration in
cypress.config.js,cypress.config.tsandcypress.json. For example:
const { defineConfig } = require('cypress')
module.exports = defineConfig({
baseUrl: 'http://localhost:1234'
})
import { defineConfig } from 'cypress'
export default defineConfig({
baseUrl: 'http://localhost:1234'
})
Deprecated
The cypress.json file is deprecated as of Cypress CFG_VERSION. We recommend
that you update your configuration. Please see the
new configuration guide and the
migration guide for more information.
{
"baseUrl": "http://localhost:1234"
}
Plugins file deprecation
Because Cypress now supports JavaScript and TypeScript configuration files, a
separate "plugins file" (which defaulted to cypress/plugins/index.js) is no
longer needed! You can do everything you used to do in the plugins file directly
inside of the Cypress configuration file.
Accordingly, the plugins file is now deprecated. It has been replaced with the
new setupNodeEvents
function and the
devServer and devServerConfig
options.
Related notes:
- The
setupNodeEventsfunction is functionally equivalent to the function exported from the plugins file; it takes the sameonandconfigarguments, and should return the same value. - The
devServeranddevServerConfigoptions are specific to component testing, and offer a much more streamlined and consistent way to configure a dev server than using the plugins file. - Many pages and examples throughout the documentation have been updated to show
configuration in
setupNodeEventsas well as the plugins file. For example:
const { defineConfig } = require('cypress')
module.exports = defineConfig({
// setupNodeEvents can be defined in either
// the e2e or component configuration
e2e: {
setupNodeEvents(on, config) {
// bind to the event we care about
on('<event>', (arg1, arg2) => {
// plugin stuff here
})
}
}
})
import { defineConfig } from 'cypress'
export default defineConfig({
// setupNodeEvents can be defined in either
// the e2e or component configuration
e2e: {
setupNodeEvents(on, config) {
// bind to the event we care about
on('<event>', (arg1, arg2) => {
// plugin stuff here
})
}
}
})
Deprecated
The plugins file is deprecated as of Cypress CFG_VERSION. We recommend that you update your configuration. Please see the plugins guide and the migration guide for more information.
// cypress/plugins/index.js
module.exports = (on, config) => {
// bind to the event we care about
on('<event>', (arg1, arg2) => {
// plugin stuff here
})
}
Config option changes
CONTENT_TBD
Migrating to Cypress 8.0
This guide details the changes and how to change your code to migrate to Cypress 8.0. See the full changelog for 8.0.
cypress run runs all browsers --headless
When running cypress run previous to 8.0, some browsers would launch headed
while others were launched headless by default. In 8.0, we've normalized all
browsers to launch as headless by default.
This could cause a couple of changes to your existing runs:
- You may see the screenshot or video resolution of runs during
cypress runchange to the default of 1280x720. This is because headless browsers use the set screen size as opposed to the browser's size when opening headed. - Chrome extensions will not load during a
--headlessrun. If your run depends on a Chrome extension being loaded duringcypress run, you should explicitly pass the--headedflag.
You can now remove the use of the --headless flag during cypress run as this
is the default for all browsers.
You should also update any use of the isHeaded or isHeadless property on
Cypress.browser or the
browser launch API accordingly.
cypress run --browser=chrome --headless
cypress run --browser=firefox --headless
--headless
flag during
cypress run
.
cypress run --browser=chrome
cypress run --browser=firefox
Default screen size during --headless
The default screen size when running a headless browser has been reverted back to 1280x720 pixels. If you have any code in the browser launch API to set the screen size to 1280x720, this can be removed.
// cypress/plugins/index.js
module.exports = (on, config) => {
on('before:browser:launch', (browser, launchOptions) => {
if (browser.name === 'chrome' && browser.isHeadless) {
launchOptions.args.push('--window-size=1280,720')
}
if (browser.name === 'electron' && browser.isHeadless) {
launchOptions.preferences.width = 1280
launchOptions.preferences.height = 720
}
if (browser.name === 'firefox' && browser.isHeadless) {
launchOptions.args.push('--width=1280')
launchOptions.args.push('--height=720')
}
return launchOptions
})
}
// cypress/plugins/index.js
module.exports = (on, config) => {
// the default screen size is 1280x720 in all headless browsers
}
Migrating to Cypress 7.0
This guide details the changes and how to change your code to migrate to Cypress 7.0. See the full changelog for 7.0.
cy.intercept() changes
Cypress 7.0 comes with some breaking
changes to cy.intercept():
Handler ordering is reversed
Previous to Cypress 7.0, cy.intercept() handlers were run in the
order that they are defined, stopping after the first handler to call
req.reply(), or once all handlers are complete.
With Cypress 7.0, cy.intercept() handlers are now run in reverse
order of definition, stopping after the first handler to call req.reply(), or
once all handlers are complete.
This change was done so that users can override previously declared
cy.intercept() handlers by calling cy.intercept()
again. See #9302 for more
details.
cy.intercept(url, (req) => {
/* This will be called first! */
})
cy.intercept(url, (req) => {
/* This will be called second! */
})
cy.intercept(url, (req) => {
/* This will be called second! */
})
cy.intercept(url, (req) => {
/* This will be called first! */
})
Read more about the cy.intercept() interception lifecycle.
URL matching is stricter
Before Cypress 7.0, cy.intercept() would match URLs against
strings by using minimatch, substring match, or by equality.
With Cypress 7.0, this behavior is being tightened - URLs are matched against
strings only by minimatch or by equality. The substring match has been
removed.
This more closely matches the URL matching behavior shown by cy.route().
However, some intercepts will not match, even though they did before.
For example, requests with querystrings may no longer match:
// will this intercept match a request for `/items?page=1`?
cy.intercept('/items')
// ✅ before 7.0.0, this will match, because it is a substring
// ❌ after 7.0.0, this will not match, because of the querystring
// solution: update the intercept to match the querystring with a wildcard:
cy.intercept('/items?*')
Also, requests for paths in nested directories may be affected:
// will this intercept match a request for `/some/items`?
cy.intercept('/items')
// ✅ before 7.0.0, this will match, because it is a substring
// ❌ after 7.0.0, this will not match, because of the leading directory
// solution: update the intercept to include the directory:
cy.intercept('/some/items')
Additionally, the matchUrlAgainstPath RouteMatcher option that was added in
Cypress 6.2.0 has been removed in Cypress 7.0. It can be safely removed from
tests.
Deprecated cy.route2() command removed
cy.route2() was the original name for cy.intercept() during the experimental
phase of the feature. It was deprecated in Cypress 6.0. In Cypress 7.0, it has
been removed entirely. Please update existing usages of cy.route2() to call
cy.intercept() instead.
cy.route2('/widgets/*', { fixture: 'widget.json' }).as('widget')
cy.intercept('/widgets/*', { fixture: 'widget.json' }).as('widget')
res.delay() and res.throttle() have been renamed
The res.delay() and res.throttle() functions that exist on responses yielded
to response handlers have been renamed.
The new names are res.setDelay() and res.setThrottle(), respectively.
cy.intercept('/slow', (req) => {
req.continue((res) => {
// apply a delay of 1 second and a throttle of 56kbps
res.delay(1000).throttle(56)
})
})
cy.intercept('/slow', (req) => {
req.continue((res) => {
// apply a delay of 1 second and a throttle of 56kbps
res.setDelay(1000).setThrottle(56)
})
})
Read more about available functions on res.
Falsy values are no longer dropped in StaticResponse bodies
Previously, falsy values supplied as the body of a StaticResponse would get
dropped (the same as if no body was supplied). Now, the bodies are properly
encoded in the response.
cy.intercept('/does-it-exist', { body: false })
// Requests to `/does-it-exist` receive an empty response body
cy.intercept('/does-it-exist', { body: false })
// Requests to `/does-it-exist` receive a response body of `false`
Errors thrown by request and response handlers are no longer wrapped
Previously, errors thrown inside of req and res handlers would be wrapped by
a CypressError. In 7.0.0, errors thrown inside of these handlers are not
wrapped before failing the test.
This should only affect users who are explicitly asserting on global errors. See #15189 for more details.
Component Testing
In 7.0, component testing is no longer experimental. Cypress now ships with a dedicated component test runner with a new UI and dedicated commands to launch it.
Changes are required for all existing projects. The required changes are
limited to configuration and there are no breaking changes to the mount API.
The migration guide contains the following steps:
- Update your Cypress configuration to remove
experimentalComponentTesting - Install updated dependencies
- Update the plugins file
- Use CLI commands to launch
- Update the support file (optionally)
1. Remove experimentalComponentTesting config
The experimentalComponentTesting configuration is no longer needed to run
component tests. Remove this flag in order to run Cypress tests without
erroring.
{
"experimentalComponentTesting": true,
"componentFolder": "src",
"testFiles": "**/*spec.{js,jsx,ts,tsx}"
}
{
"componentFolder": "src",
"testFiles": "**/*spec.{js,jsx,ts,tsx}"
}
2. Install component testing dependencies
The Component Test Runner requires the following dependencies:
- Framework-specific bindings such as
@cypress/react. - Development server adapter such as
@cypress/webpack-dev-server. - Peer dependencies such as
webpack-dev-server,vue, orreact.
Install React dependencies
- Upgrade to
@cypress/react5.X. - Install
@cypress/webpack-dev-server. - (Optional) Install
cypress-react-selectorif any tests usecy.react(). - (Optional) Install code coverage, see installation steps).
npm i cypress @cypress/react @cypress/webpack-dev-server -D
Install Vue 3 dependencies
- Upgrade to
@cypress/vue@next(3.X and above). - Install
@cypress/webpack-dev-server.
npm i cypress @cypress/vue@next @cypress/webpack-dev-server -D
Install Vue 2 dependencies
- Upgrade to
@cypress/vue@2(2.X only). - Install
@cypress/webpack-dev-server.
npm i cypress @cypress/vue @cypress/webpack-dev-server -D
3. Update plugins file to use dev-server:start
Re-using a project's local development server instead of file preprocessors
In 7.0 Cypress component tests require that code is bundled with your local
development server, via a new dev-server:start event. This event replaces the
previous file:preprocessor event.
const webpackPreprocessor = require('@cypress/webpack-preprocessor')
const webpackConfig = require('../webpack.config.js')
module.exports = (on, config) => {
on('file:preprocessor', webpackPreprocessor(options))
}
// The @cypress/webpack-dev-server package replaces @cypress/webpack-preprocessor
const { startDevServer } = require('@cypress/webpack-dev-server')
const webpackConfig = require('../webpack.config.js')
module.exports = (on, config) => {
// You must use the dev-server:start event instead of the file:preprocessor event
on('dev-server:start', (options) => {
return startDevServer({ options, webpackConfig })
})
}
Configure plugins.js for React projects
Projects using React may not need to update their plugins file. If your project
is using a webpack scaffold or boilerplate, it is recommended to use a preset
plugin imported from
@cypress/react/plugins.
Preset Plugins for React
If you are using a preset plugin within
@cypress/react, you should not
need to update your plugins file. To check if you are using a preset, check to
see if your plugins file contains an import to a file inside of
@cypress/react/plugins.
// The @cypress/react project exposes preset plugin configurations
// These presets automatically register the events to bundle the project properly
const injectReactScriptsDevServer = require('@cypress/react/plugins/react-scripts')
module.exports = (on, config) => {
// Internally, this method registers `dev-server:start` with the proper webpack configuration
// Previously, it registered the `file:preprocessor` event.
injectReactScriptsDevServer(on, config)
return config
}
Configure plugins.js for Vue
Projects using Vue will likely be using either
@vue/cli or manually defining webpack configuration.
These steps are identical to the manual setup steps, with the exception of how
you resolve the webpack configuration. To access the resolved webpack
configuration that contains any vue.config.js setup or the default
@vue/cli webpack setup, you must import the
configuration and pass it into
@cypress/webpack-dev-server.
const { startDevServer } = require('@cypress/webpack-dev-server')
// The resolved configuration, which contains any `vue.config.js` setup
const webpackConfig = require('@vue/cli-service/webpack.config.js')
module.exports = (on, config) => {
on('dev-server:start', (options) => {
return startDevServer({ options, webpackConfig })
})
}
Configuring a project with vanilla webpack
For projects with manually defined or ejected webpack configurations, the webpack configuration must be passed in.
const { startDevServer } = require('@cypress/webpack-dev-server')
const webpackConfig = require('../webpack.config.js')
module.exports = (on, config) => {
on('dev-server:start', (options) => {
return startDevServer({ options, webpackConfig })
})
}
4. Use CLI commands to launch
To run your component tests you must use the dedicated component testing subcommands.
cypress open-ctcypress run-ct
Component tests will no longer be picked up when launching Cypress from
cypress open or cypress run. Please use cypress open-ct or
cypress run-ct.
cypress run
# open component testing runner
cypress open-ct
# run all component tests
cypress run-ct
# e2e tests
cypress open
cypress run
5. Update the support file (optionally)
Previously, a support file was required to set up the component testing target node. This is no longer necessary.
Specifically for React users, if the support file contains the following line, please remove it. The import will fail in the future. We have left it in to avoid a breaking change, but the file does nothing.
// support.js
// This import should be removed, it will error in a future update
import '@cypress/react/hooks'
Expanded stylesheet support
Stylesheets are now bundled and imported within spec and support files.
Previously, many of mount's mounting options such as stylesheets,
cssFiles, and styles were required to import stylesheets into your component
tests. This often involved pre-compiling the stylesheets before launching the
component tests, which affected performance. Migrating to imports for these
styles is optional, but recommended.
Now, stylesheets should be loaded into the document the same way they are in
your application. It is recommended you update your code like so:
const { mount } = require('@cypress/react')
const Button = require('./Button')
it('renders a Button', () => {
// Mounting a button and loading the Tailwind CSS library
mount(<Button />, {
stylesheets: [
// Paths are relative to the project root directory and must be pre-compiled
// Because they are static, they do not watch for file updates
'/dist/index.css',
'/node_modules/tailwindcss/dist/tailwind.min.css',
],
})
})
mountingOptions.stylesheets
is not recommended
// In the majority of modern style-loaders,
// these styles will be injected into document.head when they're imported below
require('./index.scss')
require('tailwindcss/dist/tailwind.min.css')
const { mount } = require('@cypress/react')
const Button = require('./Button')
it('renders a Button', () => {
// This button will render with the Tailwind CSS styles
// as well as the application's index.scss styles
mount(<Button />)
})
Desktop GUI no longer displays component tests
Previously, the Desktop GUI displayed both end-to-end and component tests.
Now, component tests are only displayed when launching via the component
testing-specific subcommands. cypress open-ct (or run-ct in CI)
Executing all or some component tests
In 6.X, the Desktop GUI had support for finding and executing a subset of
component tests. In 7.0, this is possible with the --headed command and a spec
glob, like so:
cypress run-ct --headed --spec **/some-folder/*spec.*
Coverage
Previously, the @cypress/react
4.X package embedded code coverage in your tests automatically.
If you still wish to record code coverage in your tests, you must manually install it. Please see our code coverage guide for the latest steps.
cypress-react-selector
If you use cy.react() in your tests, you must manually install
cypress-react-selector
with npm i cypress-react-selector -D. You do not need to update your support
file.
HTML Side effects
As of 7.0, we only clean up components mounted by Cypress via
@cypress/react or
@cypress/vue.
We no longer automatically reset the document.body between tests. Any HTML
side effects of your component tests will carry over.
const { mount } = require('@cypress/react')
describe('Component teardown behavior', () => {
it('modifies the document and mounts a component', () => {
// HTML unrelated to the component is mounted
Cypress.$('body').append('<div id="some-html"/>')
// A component is mounted
mount(<Button id="my-button"></Button>)
cy.get('#some-html').should('exist')
cy.get('#my-button').should('exist')
})
it('cleans up any HTML', () => {
// The component is automatically unmounted by Cypress
cy.get('#my-button').should('not.exist')
// The HTML left over from the previous test has been cleaned up
// This was done automatically by Cypress
cy.get('#some-html').should('not.exist')
})
})
const { mount } = require('@cypress/react')
describe('Component teardown behavior', () => {
it('modifies the document and mounts a component', () => {
// HTML unrelated to the component is mounted
Cypress.$('body').append('<div id="some-html"/>')
// A component is mounted
mount(<Button id="my-button"></Button>)
cy.get('#some-html').should('exist')
cy.get('#my-button').should('exist')
})
it('only cleans up *components* between tests', () => {
// The component is automatically unmounted by Cypress
cy.get('#my-button').should('not.exist')
// The HTML left over from the previous test should be manually cleared
cy.get('#some-html').should('not.exist')
})
})
Legacy cypress-react-unit-test and cypress-vue-unit-test packages
For users upgrading from
cypress-react-unit-tests
or
cypress-vue-unit-tests,
please update all references to use
@cypress/react or
@cypress/vue. These packages
have been deprecated and moved to the Cypress scope on npm.
Uncaught exception and unhandled rejections
In 7.0, Cypress now fails tests in more situations where there is an uncaught exception and also if there is an unhandled promise rejection in the application under test.
You can ignore these situations and not fail the Cypress test with the code below.
Turn off all uncaught exception handling
Cypress.on('uncaught:exception', (err, runnable) => {
// returning false here prevents Cypress from
// failing the test
return false
})
Turn off uncaught exception handling unhandled promise rejections
Cypress.on('uncaught:exception', (err, runnable, promise) => {
// when the exception originated from an unhandled promise
// rejection, the promise is provided as a third argument
// you can turn off failing the test in this case
if (promise) {
// returning false here prevents Cypress from
// failing the test
return false
}
})
Node.js 12+ support
Cypress comes bundled with its own
Node.js version.
However, installing the cypress npm package uses the Node.js version installed
on your system.
Node.js 10 reached its end of life on Dec 31, 2019 and Node.js 13 reached its end of life on June 1, 2019. See Node's release schedule. These Node.js versions will no longer be supported when installing Cypress. The minimum Node.js version supported to install Cypress is Node.js 12 or Node.js 14+.
Migrating cy.route() to cy.intercept()
This guide details how to change your test code to migrate from cy.route() to
cy.intercept(). cy.server() and cy.route() are deprecated in
Cypress 6.0.0. In a future release, support for cy.server() and cy.route()
will be removed.
Please also refer to the full documentation for cy.intercept().
Match simple route
In many use cases, you can replace cy.route() with cy.intercept()
and remove the call to cy.server() (which is no longer necessary).
// Set up XHR listeners using cy.route()
cy.server()
cy.route('/users').as('getUsers')
cy.route('POST', '/project').as('createProject')
cy.route('PATCH', '/projects/*').as('updateProject')
// Intercept HTTP requests
cy.intercept('/users').as('getUsers')
cy.intercept('POST', '/project').as('createProject')
cy.intercept('PATCH', '/projects/*').as('updateProject')
Match against url and path
The url argument to cy.intercept() matches against the full url,
as opposed to the url or path in cy.route(). If you're using the url
argument in cy.intercept(), you may need to update your code
depending on the route you're trying to match.
// Match XHRs with a path or url of /users
cy.server()
cy.route({
method: 'POST',
url: '/users',
}).as('getUsers')
// Match HTTP requests with a path of /users
cy.intercept({
method: 'POST',
path: '/users',
}).as('getUsers')
// OR
// Match HTTP requests with an exact url of https://example.cypress.io/users
cy.intercept({
method: 'POST',
url: 'https://example.cypress.io/users',
}).as('getUsers')
cy.wait() object
The object returned by cy.wait() is different from intercepted HTTP requests
using cy.intercept() than the object returned from an awaited
cy.route() XHR.
// Wait for XHR from cy.route()
cy.route('POST', '/users').as('createUser')
// ...
cy.wait('@createUser').then(({ requestBody, responseBody, status }) => {
expect(status).to.eq(200)
expect(requestBody.firstName).to.eq('Jane')
expect(responseBody.firstName).to.eq('Jane')
})
// Wait for intercepted HTTP request
cy.intercept('POST', '/users').as('createUser')
// ...
cy.wait('@createUser').then(({ request, response }) => {
expect(response.statusCode).to.eq(200)
expect(request.body.name).to.eq('Jane')
expect(response.body.name).to.eq('Jane')
})
Fixtures
You can stub requests and response with fixture data by defining a fixture
property in the routeHandler argument for cy.intercept().
// Stub response with fixture data using cy.route()
cy.route('GET', '/projects', 'fx:projects')
// Stub response with fixture data using cy.intercept()
cy.intercept('GET', '/projects', {
fixture: 'projects',
})
Override intercepts
As of 7.0, newer intercepts are called before older intercepts, allowing users to override intercepts. See "Handler ordering is reversed" for more details.
Before 7.0, intercepts could not be overridden. See #9302 for more details.
Migrating to Cypress 6.0
This guide details the changes and how to change your code to migrate to Cypress 6.0. See the full changelog for 6.0.
Non-existent element assertions
Key takeway: Use .should('not.exist') to assert that an element does not
exist in the DOM (not .should('not.be.visible'), etc).
In previous versions of Cypress, there was a possibility for tests to falsely pass when asserting a negative state on non-existent elements.
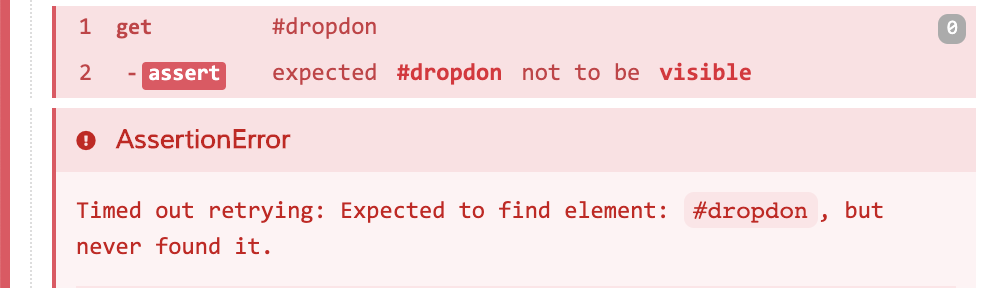
For example, in the tests below we want to test that the search dropdown is no longer visible when the search input is blurred because we hide the element in CSS styles. Except in this test, we've mistakenly misspelled one of our selectors.
cy.get('input[type=search]').type('Cypress')
cy.get('#dropdown').should('be.visible')
cy.get('input[type=search]').blur()
// below we misspelled "dropdown" in the selector 😞
// the assertions falsely pass in Cypress < 6.0
// and will correctly fail in Cypress 6.0 +
cy.get('#dropdon').should('not.be.visible')
cy.get('#dropdon').should('not.have.class', 'open')
cy.get('#dropdon').should('not.contain', 'Cypress')
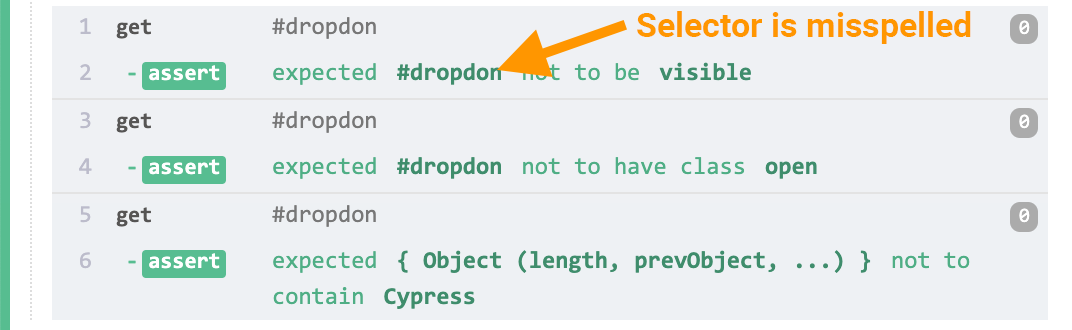
In 6.0, these assertions will now correctly fail, telling us that the #dropdon
element doesn't exist in the DOM.
Assertions on non-existent elements
This fix may cause some breaking changes in your tests if you are relying on
assertions such as not.be.visible or not.contains to test that the DOM
element did not exist in the DOM. This means you'll need to update your test
code to be more specific about your assertions on non-existent elements.
it('test', () => {
// the .modal element is removed from the DOM on click
cy.get('.modal').find('.close').click()
// assertions below pass in < 6.0, but properly fail in 6.0+
cy.get('.modal').should('not.be.visible')
cy.get('.modal').should('not.contain', 'Upgrade')
})
it('test', () => {
// the .modal element is removed from the DOM on click
cy.get('.modal').find('.close').click()
// we should instead assert that the element doesn't exist
cy.get('.modal').should('not.exist')
})
Opacity visibility
DOM elements with opacity: 0 style are no longer considered to be visible.
This includes elements with an ancestor that has opacity: 0 since a child
element can never have a computed opacity greater than that of an ancestor.
Elements where the CSS property (or ancestors) is opacity: 0 are still
considered actionable however
and
any action commands
used to interact with the element will perform the action. This matches
browser's implementation on how they regard elements with opacity: 0.
Assert visibility of opacity: 0 element
opacity: 0
element
is not visible.
it('test', () => {
// '.hidden' has 'opacity: 0' style.
// In < 5.0 this assertion would fail
cy.get('.hidden').should('not.be.visible')
})
opacity: 0
element
is not visible.
it('test', () => {
// '.hidden' has 'opacity: 0' style.
// In 6.0 this assertion will pass
cy.get('.hidden').should('not.be.visible')
})
Perform actions on opacity: 0 element
In all versions of Cypress, you can interact with elements that have
opacity: 0 style.
it('test', () => {
// '.hidden' has 'opacity: 0' style.
cy.get('.hidden').click() // ✅ clicks on element
cy.get('.hidden').type('hi') // ✅ types into element
cy.get('.hidden').check() // ✅ checks element
cy.get('.hidden').select('yes') // ✅ selects element
})
cy.wait(alias) type
cy.route() is deprecated in 6.0.0. We encourage the use of cy.intercept() instead. Due to this deprecation, the type yielded by cy.wait(alias) has changed.
WaitXHR
.
Interception
. This matches the new interception object type used for
cy.intercept()
.
Restore old behavior
If you need to restore the type behavior prior to 6.0.0 for cy.wait(alias), you can declare a global override for cy.wait() like so:
declare global {
namespace Cypress {
interface Chainable<Subject = any> {
wait(alias: string): Chainable<Cypress.WaitXHR>
}
}
}
—disable-dev-shm-usage
We now pass —disable-dev-shm-usage to the Chrome browser flags by default. If
you're passing this flag in your plugins file, you can now remove this code.
// cypress/plugins/index.js
module.exports = (on, config) => {
on('before:browser:launch', (browser = {}, launchOptions) => {
if (browser.family === 'chromium' && browser.name !== 'electron') {
launchOptions.args.push('--disable-dev-shm-usage')
}
return launchOptions
})
}
// cypress/plugins/index.js
module.exports = (on, config) => {}
Restore old behavior
If you need to remove the flag in 6.0.0+, you can follow the workaround documented here: #9242.
Migrating to Cypress 5.0
This guide details the changes and how to change your code to migrate to Cypress 5.0. See the full changelog for 5.0.
Tests retries
Test retries are available in Cypress 5.0. This means that tests can be re-run a number of times before potentially being marked as a failed test. Read the Test Retries doc for more information on how this works and how to turn on test retries.
When test retries are turned on, there will now be a screenshot taken for every failed attempt, so there could potentially be more than 1 screenshot per test failure. Read the Test Retries doc for more information on how this works.
The
cypress-plugin-retries
plugin has been deprecated in favor of test retries built into Cypress. There's
guidance below on how to migrate from the
cypress-plugin-retries
plugin to Cypress's built-in test retries.
Configure test retries via the CLI
cypress-plugin-retries
via env vars
CYPRESS_RETRIES=2 cypress run
CYPRESS_RETRIES=2 cypress run
Configure test retries in the configuration file
cypress-plugin-retries
via configuration
{
"env": {
"RETRIES": 2
}
}
{
"retries": 1
}
runModeallows you to define the number of test retries when runningcypress runopenModeallows you to define the number of test retries when runningcypress open
{
"retries": {
"runMode": 1,
"openMode": 3
}
}
Configure test retries per test
cypress-plugin-retries
via the test
it('test', () => {
Cypress.currentTest.retries(2)
})
it(
'allows user to login',
{
retries: 2,
},
() => {
// ...
}
)
runModeallows you to define the number of test retries when runningcypress runopenModeallows you to define the number of test retries when runningcypress open
it(
'allows user to login',
{
retries: {
runMode: 2,
openMode: 3,
},
},
() => {
// ...
}
)
Module API results
To more accurately reflect result data for runs with
test retries, the structure of each run's runs
array resolved from the Promise returned from cypress.run() of the Module
API has changed.
Mainly there is a new attempts Array on each test which will reflect the
result of each test retry.
results.runs
Module API results
{
// ...
"runs": [{
// ...
"hooks": [{
"hookId": "h1",
"hookName": "before each",
"title": [ "before each hook" ],
"body": "function () {\n expect(true).to.be["true"];\n}"
}],
// ...
"screenshots": [{
"screenshotId": "8ddmk",
"name": null,
"testId": "r2",
"takenAt": "2020-08-05T08:52:20.432Z",
"path": "User/janelane/my-app/cypress/screenshots/spec.js/test (failed).png",
"height": 720,
"width": 1280
}],
"stats": {
// ...
"wallClockStartedAt": "2020-08-05T08:38:37.589Z",
"wallClockEndedAt": "2018-07-11T17:53:35.675Z",
"wallClockDuration": 1171
},
"tests": [{
"testId": "r2",
"title": [ "test" ],
"state": "failed",
"body": "function () {\n expect(true).to.be["false"];\n}",
"stack": "AssertionError: expected true to be false\n' +
' at Context.eval (...cypress/integration/spec.js:5:21",
"error": "expected true to be false",
"timings": {
"lifecycle": 16,
"test": {...}
},
"failedFromHookId": null,
"wallClockStartedAt": "2020-08-05T08:38:37.589Z",
"wallClockDuration": 1171,
"videoTimestamp": 4486
}],
}],
// ...
}
results.runs
Module API results
{
// ...
"runs": [{
// ...
"hooks": [{
"hookName": "before each",
"title": [ "before each hook" ],
"body": "function () {\n expect(true).to.be["true"];\n}"
}],
// ...
"stats": {
// ...
"startedAt": "2020-08-05T08:38:37.589Z",
"endedAt": "2018-07-11T17:53:35.675Z",
"duration": 1171
},
"tests": [{
"title": [ "test" ],
"state": "failed",
"body": "function () {\n expect(true).to.be["false"];\n}",
"displayError": "AssertionError: expected true to be false\n' +
' at Context.eval (...cypress/integration/spec.js:5:21",
"attempts": [{
"state": "failed",
"error": {
"message": "expected true to be false",
"name": "AssertionError",
"stack": "AssertionError: expected true to be false\n' +
' at Context.eval (...cypress/integration/spec.js:5:21"
},
"screenshots": [{
"name": null,
"takenAt": "2020-08-05T08:52:20.432Z",
"path": "User/janelane/my-app/cypress/screenshots/spec.js/test (failed).png",
"height": 720,
"width": 1280
}],
"startedAt": "2020-08-05T08:38:37.589Z",
"duration": 1171,
"videoTimestamp": 4486
}]
}],
}],
// ...
}
Cookies whitelist option renamed
The Cypress.Cookies.defaults() whitelist option
has been renamed to preserve to more closely reflect its behavior.
whitelist
option
Cypress.Cookies.defaults({
whitelist: 'session_id',
})
preserve
option
Cypress.Cookies.defaults({
preserve: 'session_id',
})
blacklistHosts configuration renamed
The blacklistHosts configuration has been renamed to
blockHosts to more closely reflect its
behavior.
This should be updated in all places where Cypress configuration can be set
including via the Cypress configuration file, command line arguments, the
pluginsFile, Cypress.config() or environment variables.
blacklistHosts
configuration
{
"blacklistHosts": "www.google-analytics.com"
}
blockHosts
configuration
{
"blockHosts": "www.google-analytics.com"
}
Return type of Cypress.Blob changed
We updated the Blob library used
behind Cypress.Blob from 1.3.3 to 2.0.2.
The return type of the Cypress.Blob methods
arrayBufferToBlob, base64StringToBlob, binaryStringToBlob, and
dataURLToBlob have changed from Promise<Blob> to Blob.
Cypress.Blob
methods returned a Promise
Cypress.Blob.base64StringToBlob(this.logo, 'image/png').then((blob) => {
// work with the returned blob
})
Cypress.Blob
methods return a Blob
const blob = Cypress.Blob.base64StringToBlob(this.logo, 'image/png')
// work with the returned blob
cy.server() whitelist option renamed
The cy.server() whitelist option has been renamed to
ignore to more closely reflect its behavior.
whitelist
option
cy.server({
whitelist: (xhr) => {
return xhr.method === 'GET' && /\.(jsx?|html|css)(\?.*)?$/.test(xhr.url)
},
})
ignore
option
cy.server({
ignore: (xhr) => {
return xhr.method === 'GET' && /\.(jsx?|html|css)(\?.*)?$/.test(xhr.url)
},
})
Cookies sameSite property
Values yielded by cy.setCookie(),
cy.getCookie(), and
cy.getCookies() will now contain the sameSite
property if specified.
If you were using the experimentalGetCookiesSameSite configuration to get the
sameSite property previously, this should be removed.
sameSite
property.
cy.getCookie('token').then((cookie) => {
// cy.getCookie() yields a cookie object
// {
// domain: "localhost",
// expiry: 1593551644,
// httpOnly: false,
// name: "token",
// path: "/commands",
// secure: false,
// value: "123ABC"
// }
})
sameSite
property
if specified.
cy.getCookie('token').then((cookie) => {
// cy.getCookie() yields a cookie object
// {
// domain: "localhost",
// expiry: 1593551644,
// httpOnly: false,
// name: "token",
// path: "/commands",
// sameSite: "strict",
// secure: false,
// value: "123ABC"
// }
})
dirname / filename
The globals __dirname and __filename no longer include a leading slash.
__dirname
/
__filename
// cypress/integration/app_spec.js
it('include leading slash < 5.0', () => {
expect(__dirname).to.equal('/cypress/integration')
expect(__filename).to.equal('/cypress/integration/app_spec.js')
})
__dirname
/
__filename
// cypress/integration/app_spec.js
it('do not include leading slash >= 5.0', () => {
expect(__dirname).to.equal('cypress/integration')
expect(__filename).to.equal('cypress/integration/app_spec.js')
})
Linux dependencies
Running Cypress on Linux now requires the libgbm dependency (on Debian-based
systems, this is available as libgbm-dev). To install all required
dependencies on Ubuntu/Debian, you can run the script below:
apt-get install libgtk2.0-0 libgtk-3-0 libgbm-dev libnotify-dev libgconf-2-4 libnss3 libxss1 libasound2 libxtst6 xauth xvfb
TypeScript esModuleInterop
Cypress no longer forces the esModuleInterop compiler option for TypeScript to
be true for spec, support, and plugins files. We recommend setting it in your
project's tsconfig.json instead if you need to.
// tsconfig.json
{
"compilerOptions": {
"esModuleInterop": true
/* ... other compiler options ... */
}
}
TypeScript 3.4+ support
Cypress 5.0 raises minimum required TypeScript version from 2.9+ to 3.4+. You'll need to have TypeScript 3.4+ installed within your project to have TypeScript support within Cypress.
Node.js 10+ support
Cypress comes bundled with its own
Node.js version.
However, installing the cypress npm package uses the Node.js version installed
on your system.
Node.js 8 reached its end of life on Dec 31, 2019 and Node.js 11 reached its end of life on June 1, 2019. See Node's release schedule. These Node.js versions will no longer be supported when installing Cypress. The minimum Node.js version supported to install Cypress is Node.js 10 or Node.js 12+.
Migrating to Cypress 4.0
This guide details the changes and how to change your code to migrate to Cypress 4.0. See the full changelog for 4.0.
Mocha upgrade
Mocha was upgraded from 2.5.3 to 7.0.1, which includes a number of breaking
changes and new features outlined in their
changelog. Some
changes you might notice are described below.
Breaking Change: invoke done callback and return a promise
Starting with
Mocha 3.0.0,
invoking a done callback and returning a promise in a test results in an
error.
This error originates from Mocha and is discussed at length here and here.
The reason is that using two different ways to signal that a test is finished is usually a mistake and there is always a way to only use one. There is a proposal to handle this situation without erroring that may be released in a future version of Mocha.
In the meantime, you can fix the error by choosing a single way to signal the end of your test's execution.
Example #1
it('uses invokes done and returns promise', (done) => {
return codeUnderTest.doSomethingThatReturnsPromise().then((result) => {
// assertions here
done()
})
})
done
callback and
return the promise instead:
it('uses invokes done and returns promise', () => {
return codeUnderTest.doSomethingThatReturnsPromise().then((result) => {
// assertions here
})
})
Example #2
done
callback and not return a promise:
it('uses invokes done and returns promise', (done) => {
eventEmitter.on('change', () => {
// assertions
done()
})
return eventEmitter.doSomethingThatEmitsChange()
})
it('uses invokes done and returns promise', (done) => {
eventEmitter.on('change', () => {
// assertions
done()
})
eventEmitter.doSomethingThatEmitsChange()
})
Example #3
Test functions using async/await automatically return a promise, so they need
to be refactored to not use a done callback.
it('uses async/await', async (done) => {
const eventEmitter = await getEventEmitter()
eventEmitter.on('change', () => done())
eventEmitter.doSomethingThatEmitsChange()
})
it('uses async/await', async () => {
const eventEmitter = await getEventEmitter()
return new Promise((resolve) => {
eventEmitter.on('change', () => resolve())
eventEmitter.doSomethingThatEmitsChange()
})
})
Tests require a title
Tests now require a title and will error when not provided one.
// Would show as pending in Cypress 3
// Will throw type error in Cypress 4:
it() // Test argument "title" should be a string. Received type "undefined"
Chai upgrade
Chai was upgraded from 3.5.0 to 4.2.0, which includes a number of breaking
changes and new features outlined in
Chai's migration guide. Some
changes you might notice are described below.
Breaking Change: assertions expecting numbers
Some assertions will now throw an error if the assertion's target or arguments
are not numbers, including within, above, least, below, most,
increase and decrease.
// These will now throw errors:
expect(null).to.be.within(0, 1)
expect(null).to.be.above(10)
// This will not throw errors:
expect('string').to.have.a.length.of.at.least(3)
Breaking Change: empty assertions
The .empty assertion will now throw when it is passed non-string primitives
and functions.
// These will now throw TypeErrors
expect(Symbol()).to.be.empty
expect(() => {}).to.be.empty
Breaking Change: non-existent properties
An error will throw when a non-existent property is read. If there are typos in property assertions, they will now appear as failures.
// Would pass in Cypress 3 but will fail correctly in 4
expect(true).to.be.ture
Breaking Change: include checks strict equality
include now always use strict equality unless the deep property is set.
include
would always use deep equality
// Would pass in Cypress 3 but will fail correctly in 4
cy.wrap([
{
first: 'Jane',
last: 'Lane',
},
]).should('include', {
first: 'Jane',
last: 'Lane',
})
deep.include
for deep
equality
// Specifically check for deep.include to pass in Cypress 4
cy.wrap([
{
first: 'Jane',
last: 'Lane',
},
]).should('deep.include', {
first: 'Jane',
last: 'Lane',
})
Sinon.JS upgrade
Sinon.JS was upgraded from 3.2.0 to 8.1.1, which includes a number of
breaking changes and new features outlined in
Sinon.JS's migration guide.
Some changes you might notice are described below.
Breaking Change: stub non-existent properties
An error will throw when trying to stub a non-existent property.
// Would pass in Cypress 3 but will fail in 4
cy.stub(obj, 'nonExistingProperty')
Breaking Change: reset() replaced by resetHistory()
For spies and stubs, the reset() method was replaced by resetHistory().
reset()
.
const spy = cy.spy()
const stub = cy.stub()
spy.reset()
stub.reset()
resetHistory()
.
const spy = cy.spy()
const stub = cy.stub()
spy.resetHistory()
stub.resetHistory()
Plugin Event before:browser:launch
Since we now support more advanced browser launch options, during
before:browser:launch we no longer yield the second argument as an array of
browser arguments and instead yield a launchOptions object with an args
property.
You can see more examples of the new launchOptions in use in the
Browser Launch API doc.
on('before:browser:launch', (browser, args) => {
// will print a deprecation warning telling you
// to change your code to the new signature
args.push('--another-arg')
return args
})
args
property off
launchOptions
on('before:browser:launch', (browser, launchOptions) => {
launchOptions.args.push('--another-arg')
return launchOptions
})
Electron options in before:browser:launch
Previously, you could pass options to the launched Electron
BrowserWindow
in before:browser:launch by modifying the launchOptions object.
Now, you must pass those options as launchOptions.preferences:
launchOptions
object is no longer supported.
on('before:browser:launch', (browser, args) => {
args.darkTheme = true
return args
})
options.preferences
object instead.
on('before:browser:launch', (browser, launchOptions) => {
launchOptions.preferences.darkTheme = true
return launchOptions
})
Launching Chrome Canary with --browser
Before 4.0, cypress run --browser canary would run tests in Chrome Canary.
Now, you must pass --browser chrome:canary to select Chrome Canary.
See the
docs for cypress run --browser
for more information.
canary
will no longer find a
browser
cypress run --browser canary
chrome:canary
to launch Chrome Canary
cypress run --browser chrome:canary
Chromium-based browser family
We updated the Cypress browser objects of all
Chromium-based browsers, including Electron, to have chromium set as their
family field.
module.exports = (on, config) => {
on('before:browser:launch', (browser = {}, launchOptions) => {
if (browser.family === 'electron') {
// would match Electron in 3.x
// will match no browsers in 4.0.0
return launchOptions
}
if (browser.family === 'chromium') {
// would match no browsers in 3.x
// will match any Chromium-based browser in 4.0.0
// ie Chrome, Canary, Chromium, Electron, Edge (Chromium-based)
return launchOptions
}
})
}
Example #1 (Finding Electron)
module.exports = (on, config) => {
on('before:browser:launch', (browser = {}, args) => {
if (browser.family === 'electron') {
// run code for Electron browser in 3.x
return args
}
})
}
browser.name
to check for Electron
module.exports = (on, config) => {
on('before:browser:launch', (browser = {}, launchOptions) => {
if (browser.name === 'electron') {
// run code for Electron browser in 4.0.0
return launchOptions
}
})
}
Example #2 (Finding Chromium-based browsers)
module.exports = (on, config) => {
on('before:browser:launch', (browser = {}, args) => {
if (browser.family === 'chrome') {
// in 4.x, `family` was changed to 'chromium' for all Chromium-based browsers
return args
}
})
}
browser.name
and
browser.family
to
select non-Electron Chromium-based browsers
module.exports = (on, config) => {
on('before:browser:launch', (browser = {}, launchOptions) => {
if (browser.family === 'chromium' && browser.name !== 'electron') {
// pass launchOptions to Chromium-based browsers in 4.0
return launchOptions
}
})
}
cy.writeFile() yields null
cy.writeFile() now yields null instead of the contents written to the
file. This change was made to more closely align with the behavior of Node.js
fs.writeFile.
cy.writeFile('path/to/message.txt', 'Hello World').then((text) => {
// Would pass in Cypress 3 but will fail in 4
expect(text).to.equal('Hello World') // false
})
cy.writeFile('path/to/message.txt', 'Hello World')
cy.readFile('path/to/message.txt').then((text) => {
expect(text).to.equal('Hello World') // true
})
cy.contains() ignores invisible whitespaces
Browsers ignore leading, trailing, duplicate whitespaces. And Cypress now does that, too.
<p>hello world</p>
cy.get('p').contains('hello world') // Fail in 3.x. Pass in 4.0.0.
cy.get('p').contains('hello\nworld') // Pass in 3.x. Fail in 4.0.0.
Node.js 8+ support
Cypress comes bundled with its own
Node.js version.
However, installing the cypress npm package uses the Node.js version installed
on your system.
Node.js 4 reached its end of life on April 30, 2018 and Node.js 6 reached its end of life on April 30, 2019. See Node's release schedule. These Node.js versions will no longer be supported when installing Cypress. The minimum Node.js version supported to install Cypress is Node.js 8.
CJSX is no longer supported
Cypress no longer supports CJSX (CoffeeScript + JSX), because the library used to transpile it is no longer maintained.
If you need CJSX support, you can use a pre-2.x version of the Browserify preprocessor.
npm install @cypress/browserify-preprocessor@1.1.2
// cypress/plugins/index.js
const browserify = require('@cypress/browserify-preprocessor')
module.exports = (on) => {
on('file:preprocessor', browserify())
}